- 0
- List Item
- 077 2202 8588
- info@leechtherapycentre.com
Any inflammation of the joint is typically accompanied by swelling and some venous stasis. A local decrease in blood flow immediately affects the drainage of the inflammation site: the waste products are not removed in time and accumulate, which causes swelling and pain due to pressure on surrounding tissues. Obstructed blood circulation also means that supply of nutrients and oxygen is delayed to cells which need healing, which slows down the recovery. Furthermore, the immune cells cannot move fast enough in viscous blood.
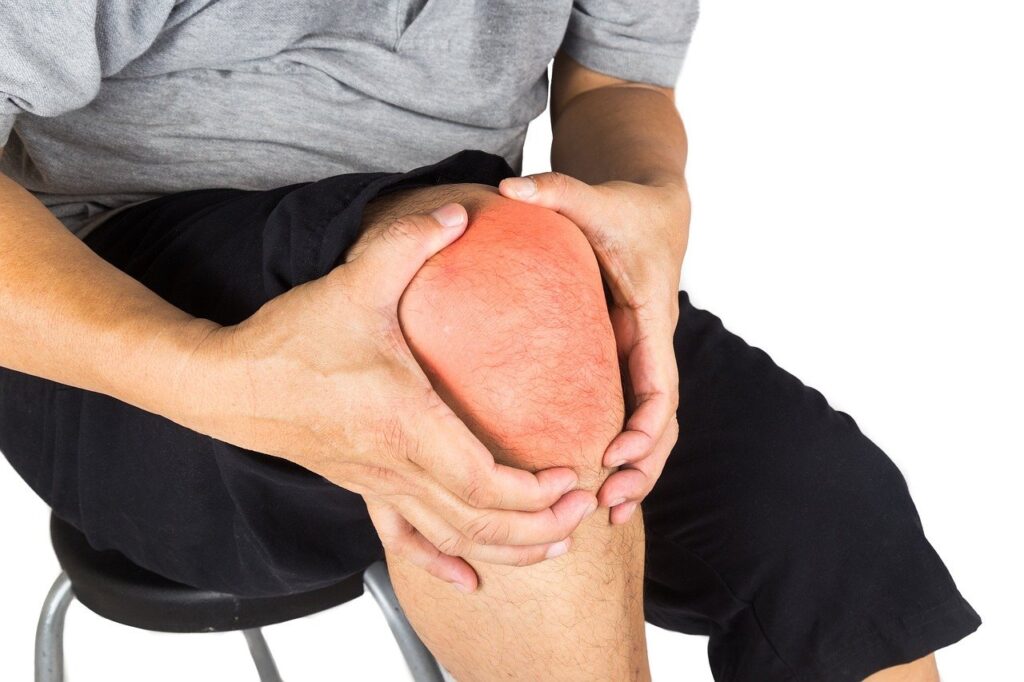
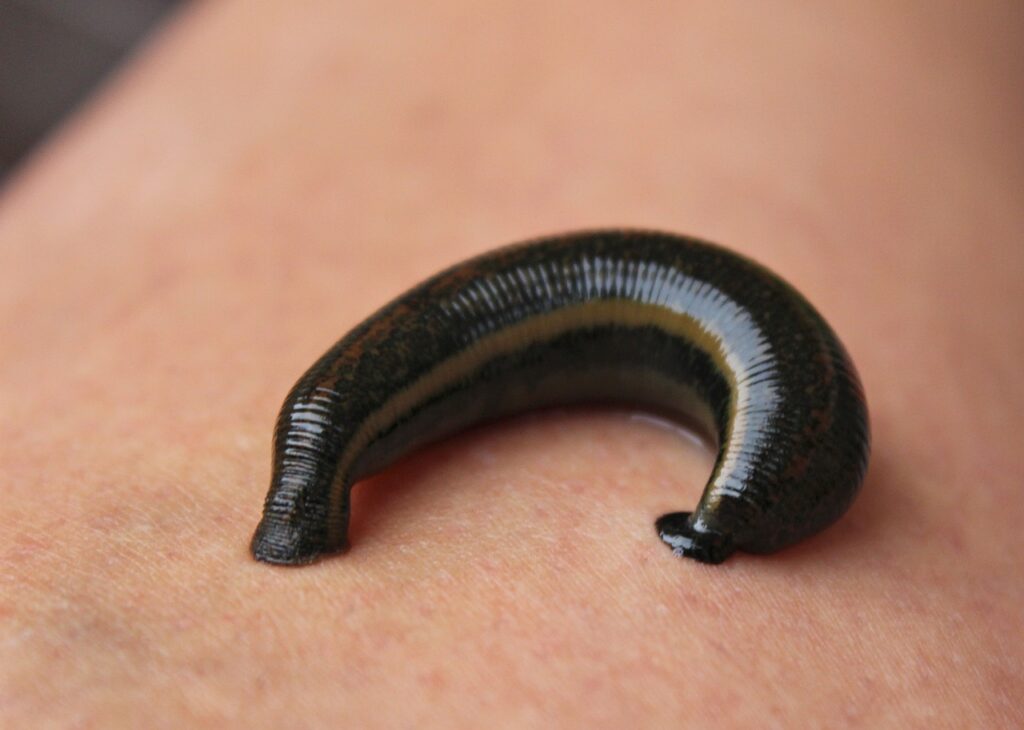
Hirudin and coalin enzymes in leech saliva are strong natural blood thinners and can help reduce blood viscosity. Hyaluronidase enzyme can help reduce oedema and swelling. It also helps to restore interstitial pressure – the outflow of decay products begins, the inflow of oxygen and nutrients improves. It also promotes the decrease in swelling of the intercellular spaces, and the activation of immune processes.
The leech saliva greatly improves blood microcirculation, unloads the venous system, reduces the aggregation of blood clots, improves blood flow speed and eliminates microthrombus. Due to the restoration of capillary circulation and lymphatic drainage, the process of inflammation starts to reduce. In addition, bradykinins, eglins and bdelins in leech saliva all have strong anti-inflammatory properties, while kininase acts as a painkiller.

© 2025 Leech Therapy Centre UK | All Rights Reserved